Z-drugs were first introduced into the mainstream market in the 1980s and 1990s [1] and have since only been approved for the short-term treatment of insomnia [2; 3].
Examples of z-drugs include the most well-known Zopiclone, which is currently a Schedule IV drug in the USA.
Zopiclone is more widely prescribed than traditional benzodiazepines [4].
They work in such a manner where they slow activity of the brain, and if used correctly can assist in your quest to get a good night’s sleep.
Over the years, and particularly more recently, zopiclone has become one of the most prescribed hypnotics in the UK [5].
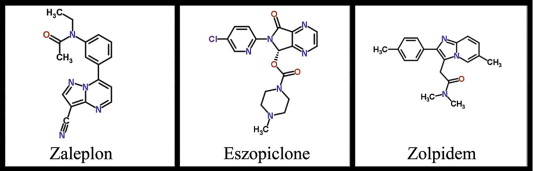
Zopiclone is one of three well-known Z-drugs – Zopiclone, Zolpidem and Zaleplon.
Z-drugs work in a similar way to benzodiazepines, however they are structurally different.
In fact, Z-drugs were made in an attempt to reduce the overall side effects that were originally described from using benzodiazepines [4].
Since hypnotic drugs like zopiclone, zaleplon and zolpidem are not considered benzodiazepine drugs, they have now become the most widely prescribed hypnotic drugs [6].
A few differences stand out between the three Z-drugs.
Of particular significance is their individual duration of action, with zopiclone having the longest duration of action [7].
More on the half-life properties and bioavailability will be discussed below.
Pharmacokinetic studies have shown that all Z-drugs, Zopiclone, Zolpidem and Zaleplon, have differing oral bioavailability, elimination rates from the body, and dose ranges.
In terms of the amount of drug that the body can readily absorb (bioavailability), The following values can be observed:[8]
- 80% – Zopiclone
- 70% – Zolpidem
- 30% – Zaleplon (which is quite low)
Each bind to the same receptor in the body; that is, the GABA receptor.
However, differences exist between all three z-drugs, namely that – once consumed these hypnotics have varying absorption profiles in the body.
Choosing between Zopiclone and Zolpidem will then largely be dependent on which period of the night one wants to cover (see Table 1).
Duration (half life)
The ways in which zolpidem and zopiclone differ can largely be attributed to their elimination half-life – the amount of time these hypnotics last in the body, once absorbed [3].
For example:
Zopiclone has a half-life of 4 to 5 hours
Zolpidem has a half-life of 2.5 hours [9; 3]
Selectivity
In addition to this information, when considering how ‘selective’ the binding of z-drugs to their GABA receptor, zopiclone differs from zolpidem in that zopiclone is less selective in its binding to several of the units that make up the GABA receptor [10].
Selectivity can sometimes be loosely attributed to potency, meaning that:
the higher the selectivity the higher the potency of the drug.
These results assessed binding selectivity both in the body and in cell culturing [10].
When comparing zaleplon to zolpidem, one study found that zaleplon had a faster elimination half-life (1 hour) matched up against zolpidem [11].
More specifically, what this research showed was that zolpidem was much slower at clearing itself from male volunteers – taking between 2-2.2 hours – with a lower oral clearance from the body [11].
This essentially means that zaleplon should exit the body faster than zolpidem.
This seemed to be especially apparent in males.
It has been previously reported in the scientific literature that:
zaleplon and zolpidem should be used very cautiously in people with depression [12].
Moreover, zaleplon and zolpidem are not recommended if an individual has a history of alcohol abuse and addiction [12].
The reason for this is due to the fact that alcohol may boost the sedative properties of z-drugs; hence the combination of any z-drugs and alcohol should be avoided.
These Z-drugs were made with a better, more improved, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profile compared to the traditional sleeping tablets on the market.
Further to this, all Z-drugs act by binding to the GABA receptor complex; like most familiar benzodiazepine drugs [9].
Having said that, there is a similarity that exists between the Z-drugs and benzodiazepine drugs; that is, they both have a very similar mode of action on GABA receptors [9].
Interestingly, zopiclone has a chemical structure to other Z-drugs (see below), such as zolpidem and other central nervous system (CNS) depressants [9].
[1] https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/13803395.2014.928268
[2] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28865038
[3] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30722037
[4] https://www.progressnp.com/article/z-hypnotics-versus-benzodiazepines-for-the-treatment-of-insomnia/
[5] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2418994/pdf/bjgp58-417.pdf
[6] https://www.bmj.com/content/345/bmj.e8343
[7] https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/psb.1061
[8] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12751920
[9] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9506247
[10] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2418994/pdf/bjgp58-417.pdf
[11] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9834048
[12] https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/psb.1061